- Search in all Repository
- Literature and maps
- Archeology
- Mills database
- Natural sciences
Advanced search
Advanced search
Advanced search
Advanced search
Advanced search

Object
Title: File of histopathological evaluation of nervous system diseases (1965) - nr 69/65
Institutional creator:
Department of Experimental and Clinical Neuropathology MMRI
Contributor:
Place of publishing:
Description:
Clinical, anatomical and histological diagnosis
Abstract:
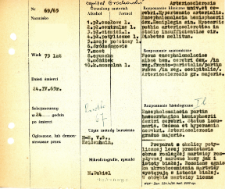
Histological diagnosis: Encephalomalacia partim haemorrhagica hemisphaerii Dextri cerebri. Stus lacunaris. Oedema et hyperaemia cerebri. Artiosclerosis gradus majoris. Autopsy examination of 75-year-old patient was performed. Neuropathological evaluation in light microscopy was based on brain paraffin sections stained with H-E, Heidenhain and Van Gieson's method.There was extensive diffuse necrosis involving both the cortex and white matter in the left occipital region. In the white matter scattered foci of hemorrhagic necrosis were seen. Cellular infiltrates consisting mostly of multinuclear leukocytes were found within the necrotic area. Macrophages also appeared in the perivascular infiltrates. At the border of necrosis there was visible malacia, and similar findings were observed in the insular cortex. Specimens of the left hemisphere contained areas of spongiosis of the frontal, parietal and amonal cortex. Loss of nerve cells was noticed, but layering was preserved. Extravasated blood was present in the subarachnoid space. Significant cellular and fibrous reaction of the soft meninges was observed. In the midbrain, spongiosis within the substancia nigra was evident. Features of edema and congestion were seen throughout the brain. The larger caliber arteries had moderately hypertrophied and fibrotic muscular layer. Smaller arteries and arterioles showed predominantly fibrotic changes without marked luminal narrowing. No vitreous changes were seen.
Format:
Resource Identifier:
Language:
Language of abstract:
Rights:
Creative Commons Attribution BY 4.0 license
Terms of use:
Copyright-protected material. [CC BY 4.0] May be used within the scope specified in Creative Commons Attribution BY 4.0 license, full text available at: ; -
Digitizing institution:
Mossakowski Medical Research Institute PAS
Original in:
Library of the Mossakowski Medical Research Institute PAS
Projects co-financed by:
Access:
Object collections:
- Digital Repository of Scientific Institutes > Scientific data and objects > Medical science > File of medical cases
- Digital Repository of Scientific Institutes > Partners' collections > Mossakowski Medical Research Institute PAS > Research data > File of histopathological evaluation of the nervous system diseases of the Department of Neuropathologu
Last modified:
Feb 1, 2022
In our library since:
Jul 9, 2021
Number of object content downloads / hits:
45
All available object's versions:
https://rcin.org.pl./publication/232813
Show description in RDF format:
Show description in RDFa format:
Show description in OAI-PMH format:
| Edition name | Date |
|---|---|
| opis nr 69/65 | Feb 1, 2022 |

 INSTYTUT ARCHEOLOGII I ETNOLOGII POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT ARCHEOLOGII I ETNOLOGII POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT BADAŃ LITERACKICH POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT BADAŃ LITERACKICH POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT BADAWCZY LEŚNICTWA
INSTYTUT BADAWCZY LEŚNICTWA
 INSTYTUT BIOLOGII DOŚWIADCZALNEJ IM. MARCELEGO NENCKIEGO POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT BIOLOGII DOŚWIADCZALNEJ IM. MARCELEGO NENCKIEGO POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT BIOLOGII SSAKÓW POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT BIOLOGII SSAKÓW POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT CHEMII FIZYCZNEJ PAN
INSTYTUT CHEMII FIZYCZNEJ PAN
 INSTYTUT CHEMII ORGANICZNEJ PAN
INSTYTUT CHEMII ORGANICZNEJ PAN
 INSTYTUT FILOZOFII I SOCJOLOGII PAN
INSTYTUT FILOZOFII I SOCJOLOGII PAN
 INSTYTUT GEOGRAFII I PRZESTRZENNEGO ZAGOSPODAROWANIA PAN
INSTYTUT GEOGRAFII I PRZESTRZENNEGO ZAGOSPODAROWANIA PAN
 INSTYTUT HISTORII im. TADEUSZA MANTEUFFLA POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT HISTORII im. TADEUSZA MANTEUFFLA POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT JĘZYKA POLSKIEGO POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT JĘZYKA POLSKIEGO POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT MATEMATYCZNY PAN
INSTYTUT MATEMATYCZNY PAN
 INSTYTUT MEDYCYNY DOŚWIADCZALNEJ I KLINICZNEJ IM.MIROSŁAWA MOSSAKOWSKIEGO POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT MEDYCYNY DOŚWIADCZALNEJ I KLINICZNEJ IM.MIROSŁAWA MOSSAKOWSKIEGO POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT PODSTAWOWYCH PROBLEMÓW TECHNIKI PAN
INSTYTUT PODSTAWOWYCH PROBLEMÓW TECHNIKI PAN
 INSTYTUT SLAWISTYKI PAN
INSTYTUT SLAWISTYKI PAN
 SIEĆ BADAWCZA ŁUKASIEWICZ - INSTYTUT TECHNOLOGII MATERIAŁÓW ELEKTRONICZNYCH
SIEĆ BADAWCZA ŁUKASIEWICZ - INSTYTUT TECHNOLOGII MATERIAŁÓW ELEKTRONICZNYCH
 MUZEUM I INSTYTUT ZOOLOGII POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
MUZEUM I INSTYTUT ZOOLOGII POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
 INSTYTUT BADAŃ SYSTEMOWYCH PAN
INSTYTUT BADAŃ SYSTEMOWYCH PAN
 INSTYTUT BOTANIKI IM. WŁADYSŁAWA SZAFERA POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK
INSTYTUT BOTANIKI IM. WŁADYSŁAWA SZAFERA POLSKIEJ AKADEMII NAUK